Sols 4437-4438: Coordinating our Dance Moves
Earth planning date: Monday, Jan. 27, 2025 I was Geology and Mineralogy (Geo) Science Team lead today, and my day started with a bang and a drum roll — delivered by a rare winter thunderstorm (rare here in England, at least). I did lose power for a few minutes, but thanks to laptop batteries and […]

4 min read
Sols 4437-4438: Coordinating our Dance Moves
Earth planning date: Monday, Jan. 27, 2025
I was Geology and Mineralogy (Geo) Science Team lead today, and my day started with a bang and a drum roll — delivered by a rare winter thunderstorm (rare here in England, at least). I did lose power for a few minutes, but thanks to laptop batteries and phone Wi-Fi, I think no one noticed … so, shhh, don’t tell the boss!
Planning was especially interesting as we had a decision to make, whether we want to align ChemCam and APXS observations with each other and focus on one target, or whether we want two different targets. As Geo Science Team lead, it is my role to facilitate this discussion, but that is always fun — and easy. Many colleagues come with well-prepared reasons for why they want to have a certain observation in today’s plan, and I always learn something new about Mars, or geology, or both when those discussions happen. Weighing all arguments carefully, we decided for the coordinated dance of contact and remote science observations on a bedrock target we named “Desert View.” APXS will start the dance, followed by ChemCam active and one RMI image on the same location. Closing out the dance will be MAHLI, by imaging the APXS target that at this point will have the laser pits.
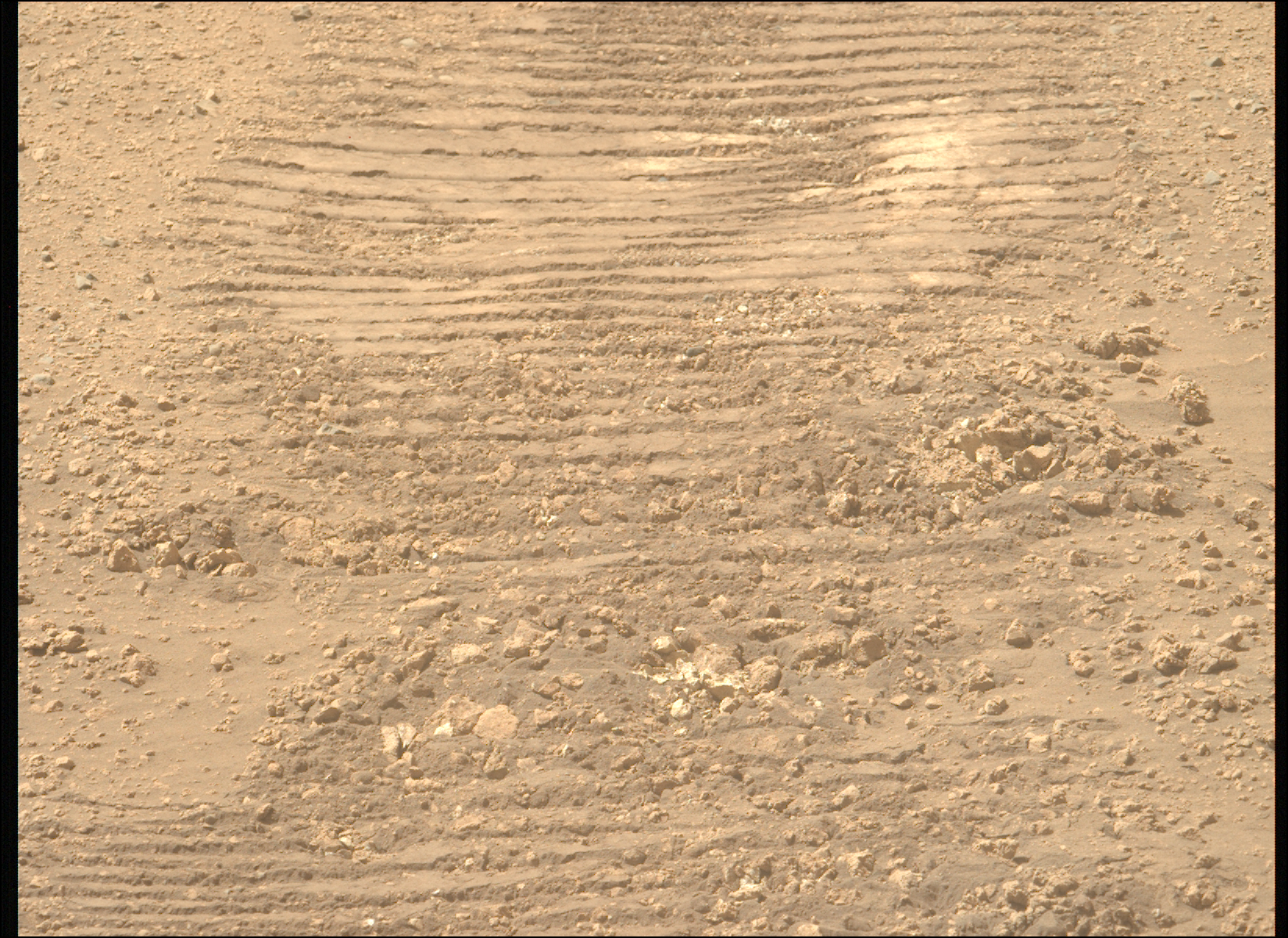
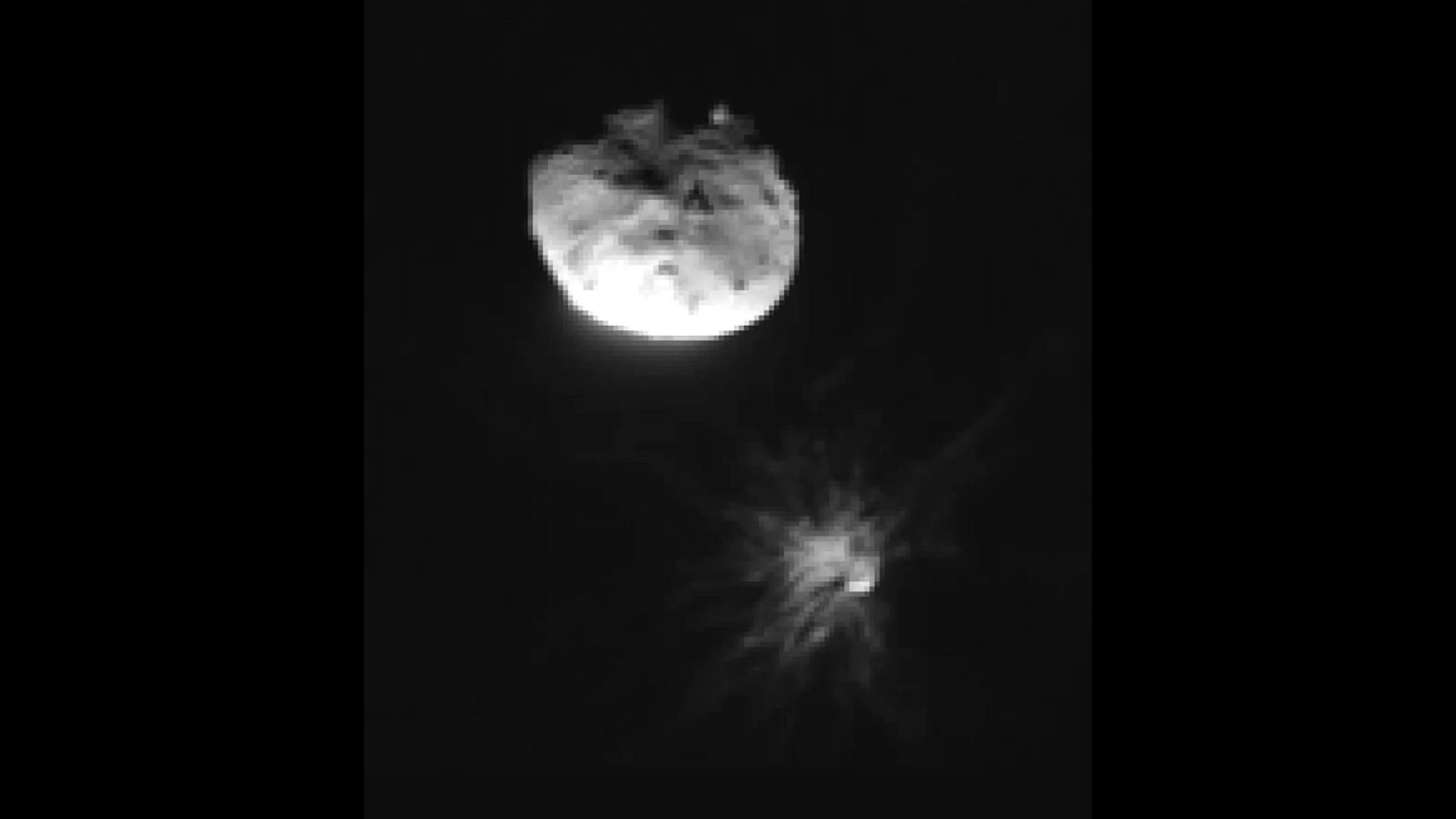
Such a coordinated observation will allow us to see how the rock reacts to the interaction with the laser. We have done this many times, and often learnt interesting things about the mineralogy of the rock. But more than 10 years ago, there was an even more ambitious coordination exercise: On sol 687 the imaging on a target called “Nova” was timed so that Mastcam actually captured the laser spark in the image. While that’s useful for engineering purposes, as a mineralogist I want to see the effect on the rock. Here is the result of that “spark” on target Nova on sol 687.
But back to today’s planning. Apart from the coordinated observations, ChemCam also adds to the Remote Micro Imager coverage of Gould Mesa with a vertical RMI observation that is designed to cover all the nice layers in the mesa, just like a stratigraphic column. Mastcam is looking back at the Rustic Canyon crater to get a new angle. Craters are three-dimensional and looking at it from all sides will help decipher the nature of this small crater, and also make full use of the window into the underground that it offers. Mastcam has two more mosaics, “Condor Peak” and “Boulder Basin,” which are both looking at interesting features in the landscape: Condor Peak at a newly visible butte, and Boulder Basin at bedrock targets in the near-field, to ascertain the structures and textures are still the same as they have been, or document any possible changes. Mars has surprised us before, so we try to look as often as power and other resources allow, even if only to confirm that nothing has changed. You can see the blocks that we are using for this observation in the grayscale Navigation Camera image above; we especially like it when upturned blocks give us a different view, while flat lying blocks in the same image show the “regular” perspective.
After the targeted science is completed, the rover will continue its drive along the planned route, to see what Mars has to offer on the next stop. After the drive, MARDI will take its image, and ChemCam do an autonomous observation, picking its own target. Also after the drive is a set of atmospheric observations to look at dust levels and search for dust devils. Continuous observations throughout include the DAN instrument’s observation of the surface and measurements of wind and temperature.
With that, the plan is again making best use of all the power we have available… and here in England the weather has improved, inside my power is back to normal, and outside it’s all back to the proverbial rain this small island is so famous for.
Written by Susanne Schwenzer, Planetary Geologist at The Open University
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)