Sols 4291-4293: Fairview Dome, the Sequel
Earth planning date: Friday, Aug. 30, 2024 Our backwards drive to “McDonald Pass” got hung up on the steep slopes of “Fairview Dome,” but unlike a lot of movie sequels, our inadvertent return visit to Fairview Dome was at least as good as the original. We took full advantage of the chance to investigate this […]

3 min read
Sols 4291-4293: Fairview Dome, the Sequel

Earth planning date: Friday, Aug. 30, 2024
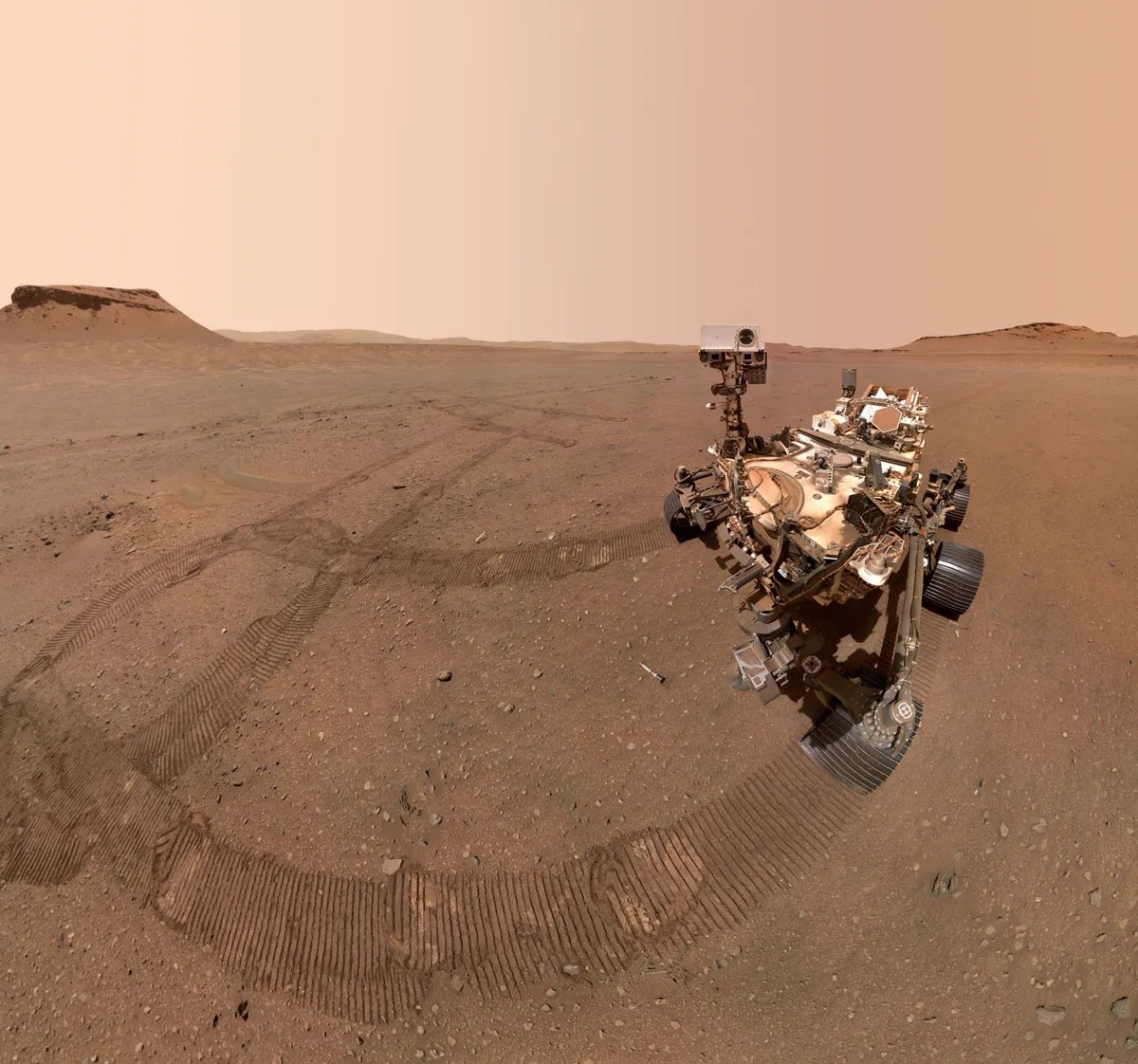
Our backwards drive to “McDonald Pass” got hung up on the steep slopes of “Fairview Dome,” but unlike a lot of movie sequels, our inadvertent return visit to Fairview Dome was at least as good as the original. We took full advantage of the chance to investigate this bedrock rise within Gediz Vallis with multiple contact and remote science targets.
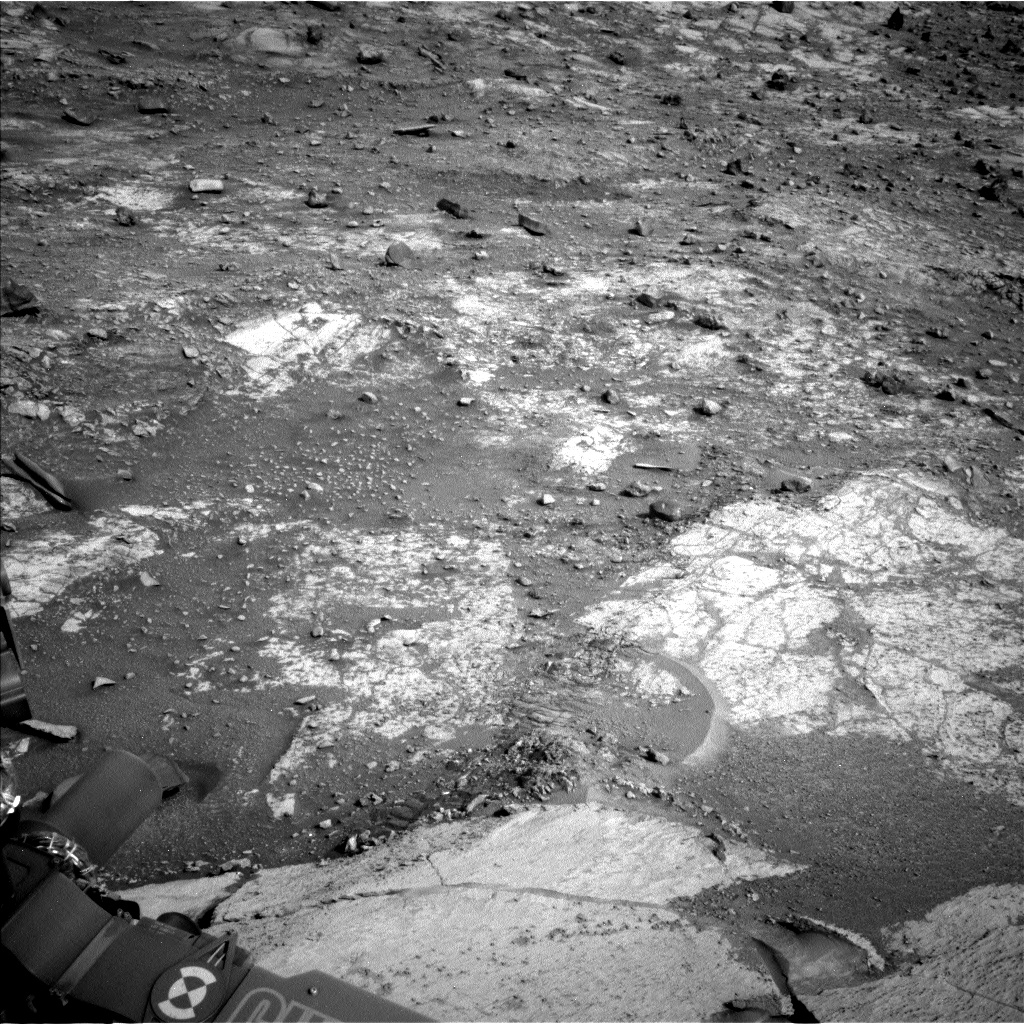
MAHLI and APXS paired up on two different DRT targets of more- and less-nodular spots of bedrock at “Lower Boy Scout Lake” and “Upper Boy Scout Lake.” You can see in the Navcam image above that just beyond the bedrock slab we stopped on, there is a wheel track and a shattered batch of rock. We crushed that bit of rock as we drove backward and were left with a great view of it, including some intriguing bright rock interiors. ChemCam targeted one of those bright rock faces at “North Palisade” and Mastcam acquired a mosaic across the whole field of broken rocks at “Ritter-Banner Saddle.” The churned-up sand of Ritter-Banner Saddle also made for a convenient change detection target as we keep our eye on the wind effects of a potential dust storm rising on Mars. ChemCam had two other opportunities for LIBS analyses at a nodular bedrock target called “Regulation Peak,” and another intriguing vertical rock face with strong color differences called “Simmons Peak.” ChemCam used RMI mosaics to image a collection of higher albedo rocks in Gediz Vallis at a site called “Buckeye Ridge.” Mastcam planned a mosaic of a different part of Gediz Vallis that is in the direction we are driving next, which will help plot those drives and also give us some insight into the boulders strewn about that part of the valley. Closer to the rover, the “Outguard Spire” target was of interest for Mastcam imaging because of its color zonation — the way colors are distributed across different areas, or zones, of the rock. It’s the kind of zonation we intend to study at McDonald Pass. The trough of sand at the “Whitney-Russell Pass” target was of interest for its potential insights into how bedrock blocks break up on Mars.
Monitoring the potential rise of a dust storm meant that the plan was busy with environmental observations. ChemCam acquired a passive sky observation, Navcam collected two rounds of dust-devil imaging, cloud movies, and atmospheric dust measurements, Mastcam acquired multiple atmospheric dust measurements, and REMS ran in longer blocks throughout each sol than it does in normal weather conditions. Dust or not, RAD and DAN passive were planned regularly through the three sols of the plan.
Written by Michelle Minitti, Planetary Geologist at Framework
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)