Navigating a Slanted River
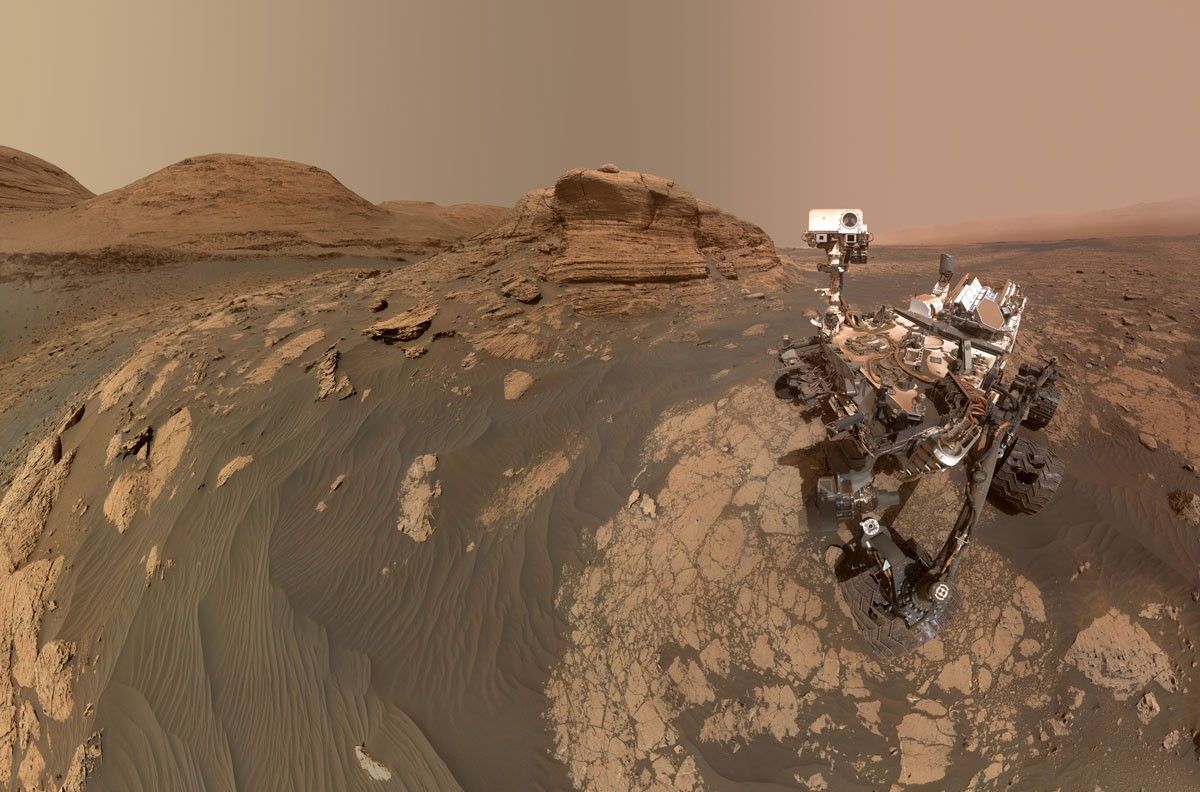
Written by Denise Buckner, student collaborator at University of Florida Perseverance is hard at work on Mars, overcoming obstacles for scientific exploration! Just a few sols after successfully sealing the challenging Green Gardens core, Perseverance roved on to the Broom Point workspace to collect another sample called Main River. Broom Point is situated a few […]

2 min read
Navigating a Slanted River

Written by Denise Buckner, student collaborator at University of Florida
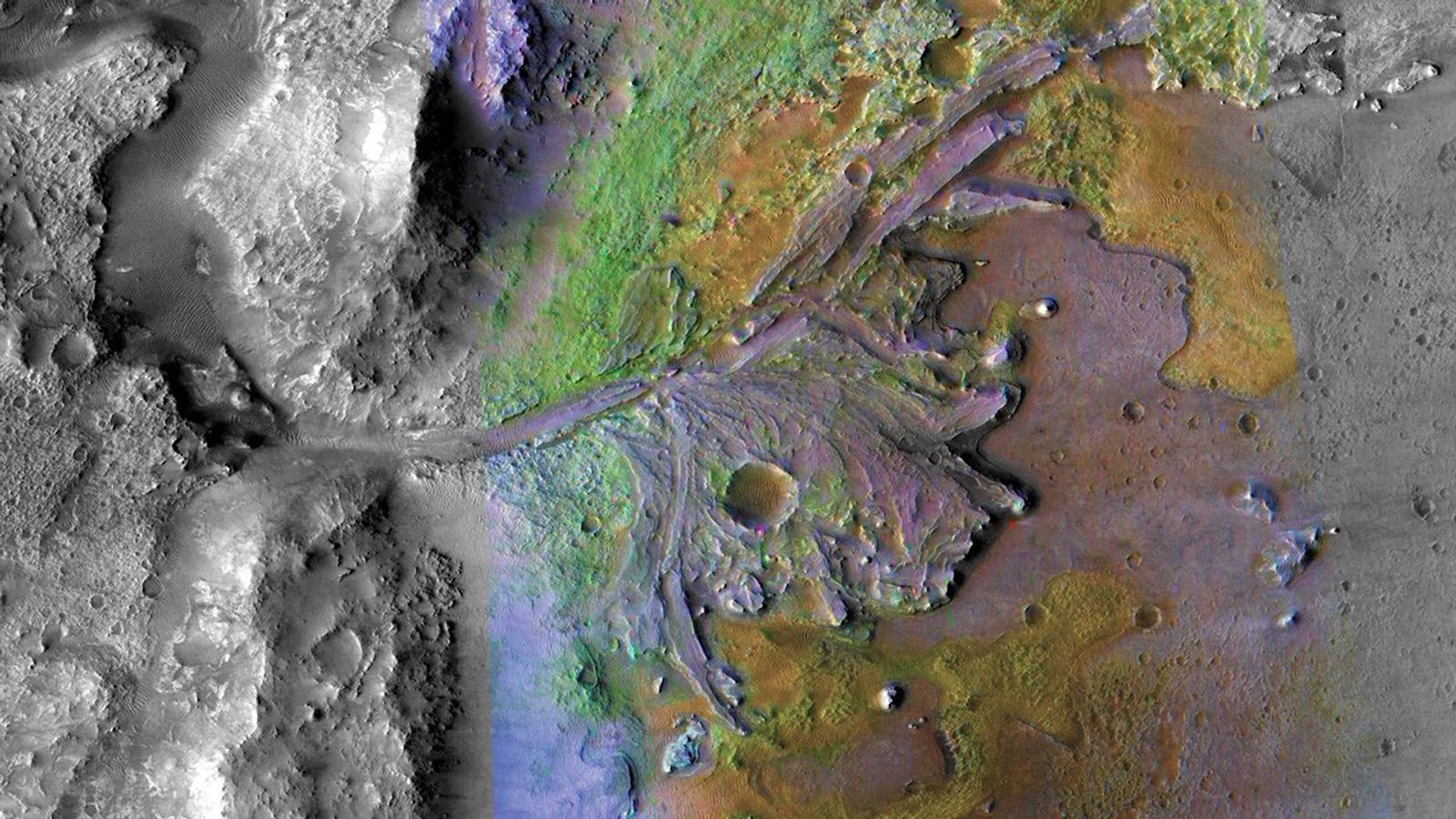
Perseverance is hard at work on Mars, overcoming obstacles for scientific exploration! Just a few sols after successfully sealing the challenging Green Gardens core, Perseverance roved on to the Broom Point workspace to collect another sample called Main River. Broom Point is situated a few hundred meters down-slope from where Green Gardens was collected, and the Science Team chose to explore this area because orbiter images show some intriguing, alternating light and dark layers.
Upon reaching the workspace, images captured by Perseverance confirm that these distinct layers are visible on the ground, as well. Layers are interesting because they record different geological events that occurred in the planet’s past, which may include deposition of sediments, lava flows, or volcanic ash. By conducting proximity science with rover instruments and collecting a core to return to Earth for future analyses, the team is investigating what this material is composed of and how it was emplaced.
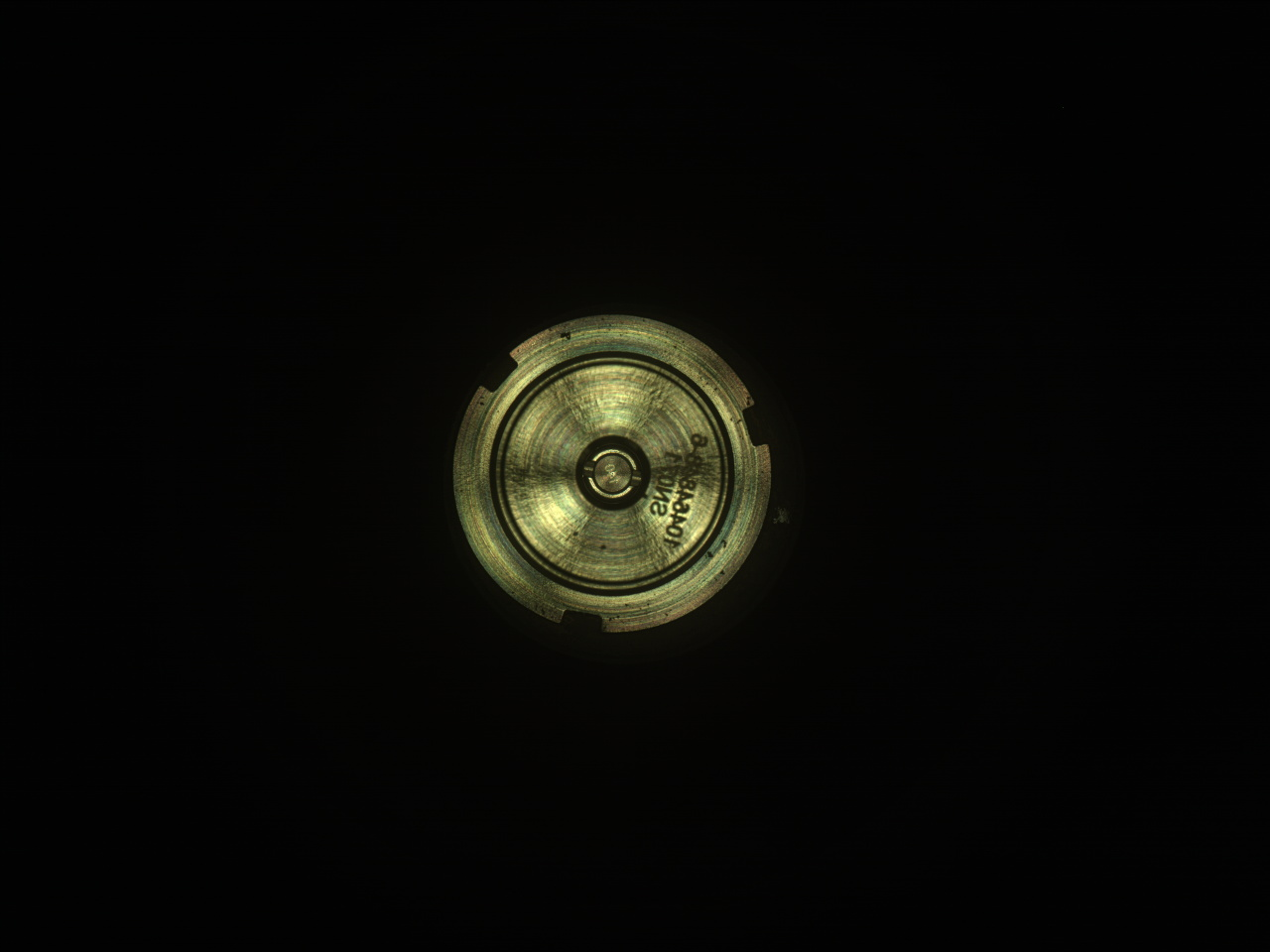
When the team is planning to collect a sample from an outcrop, the first step is to abrade the rock, grinding away the top few millimeters and smoothing out the surface so the SHERLOC and PIXL instruments can move in and conduct their scans. Although Perseverance has abraded more than 30 rocks across Jezero crater, new rocks still present unique challenges. While abrading the Slants River target at Broom Point, the rock unexpectedly fractured, resulting in an uneven surface. SHERLOC and PIXL require just a few millimeters of clearance to safely approach the rock, and while PIXL was able to reach the broken surface, the topography looked a little more dicey for SHERLOC.
The team’s engineers and rover planners took stock of the situation and decided to use WATSON, SHERLOC’s companion camera, to snap some images of the abrasion patch from another angle. These images built a surface model of the small cracks and crevices, and with this knowledge in hand, the team found a way to safely maneuver the instrument to the same spot that PIXL scanned, and collected a co-located spectroscopy map. Once this abrasion proximity science was completed, the rover went on to drill and seal the Main River core, an activity that went off without a hitch.
With another core in the bag, Perseverance is off to the next workspace, ready to tackle whatever challenges may lie ahead!
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)