NASA Shares Orion Heat Shield Findings, Updates Artemis Moon Missions
Lee esta historia en español aquí. Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the next American astronauts and first international astronaut on the South Pole region of the Moon. On Thursday, NASA announced the latest updates to its lunar exploration plans. Experts discussed results of NASA’s investigation into its Orion spacecraft heat shield after it […]

Lee esta historia en español aquí.
Through the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the next American astronauts and first international astronaut on the South Pole region of the Moon. On Thursday, NASA announced the latest updates to its lunar exploration plans.
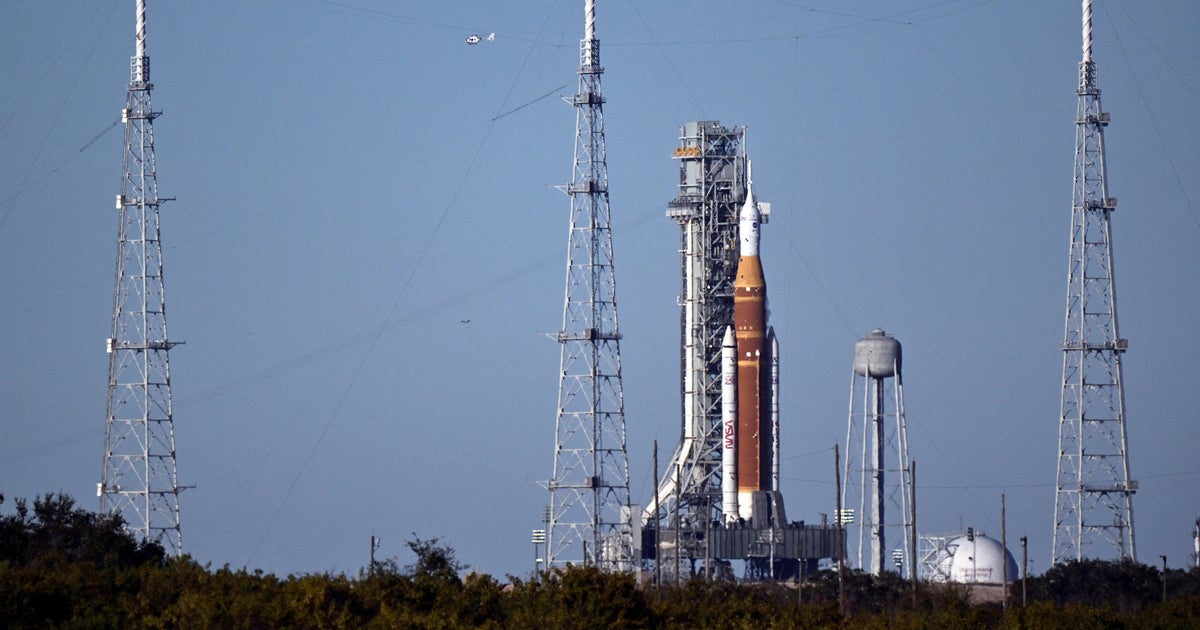
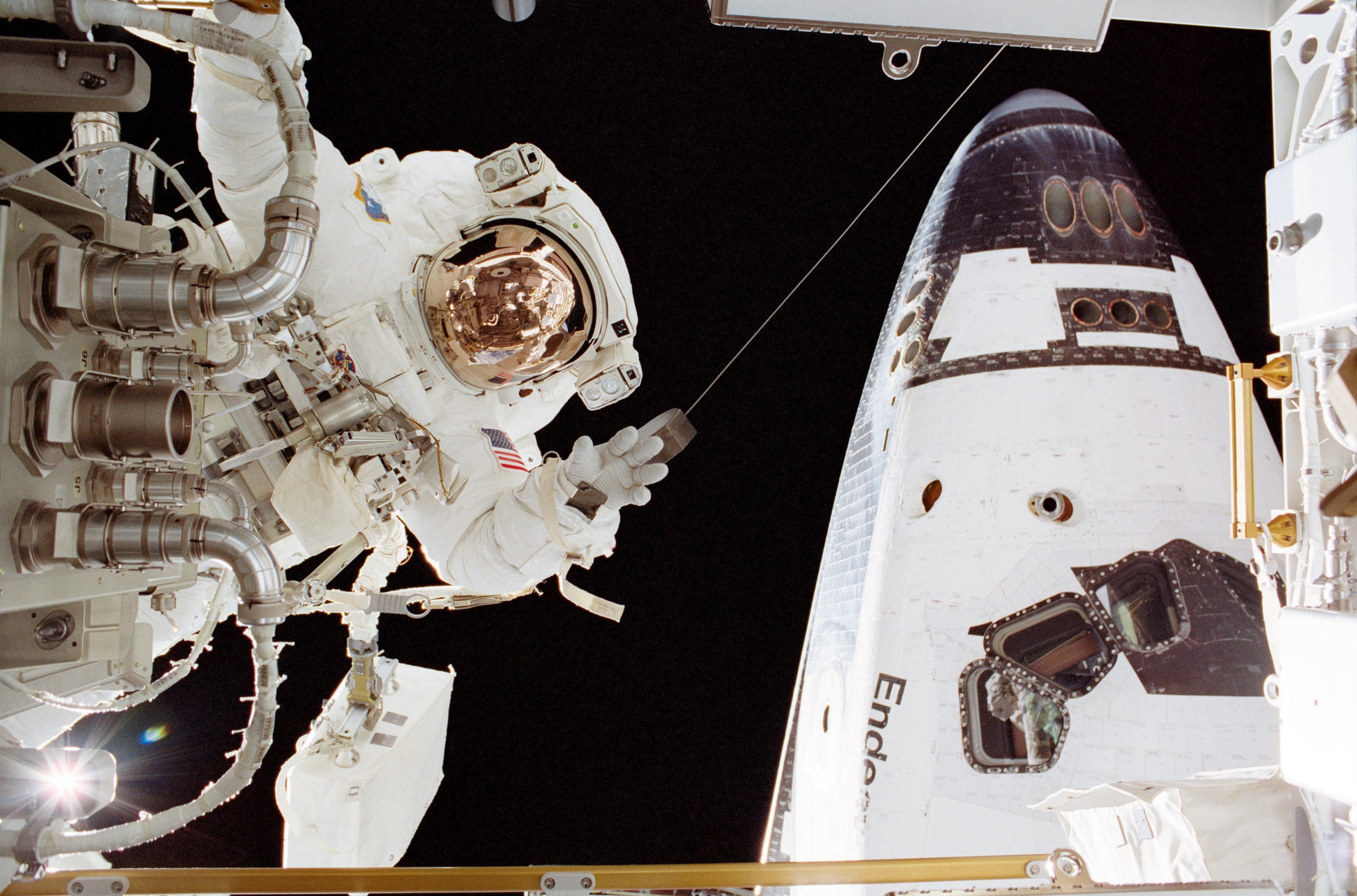
Experts discussed results of NASA’s investigation into its Orion spacecraft heat shield after it experienced an unexpected loss of charred material during re-entry of the Artemis I uncrewed test flight. For the Artemis II crewed test flight, engineers will continue to prepare Orion with the heat shield already attached to the capsule. The agency also announced it is now targeting April 2026 for Artemis II and mid-2027 for Artemis III. The updated mission timelines also reflect time to address the Orion environmental control and life support systems.
“The Artemis campaign is the most daring, technically challenging, collaborative, international endeavor humanity has ever set out to do,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “We have made significant progress on the Artemis campaign over the past four years, and I’m proud of the work our teams have done to prepare us for this next step forward in exploration as we look to learn more about Orion’s life support systems to sustain crew operations during Artemis II. We need to get this next test flight right. That’s how the Artemis campaign succeeds.”
The agency’s decision comes after an extensive investigation of an Artemis I heat shield issue showed the Artemis II heat shield can keep the crew safe during the planned mission with changes to Orion’s trajectory as it enters Earth’s atmosphere and slows from nearly 25,000 mph to about 325 mph before its parachutes unfurl for safe splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
“Throughout our process to investigate the heat shield phenomenon and determine a forward path, we’ve stayed true to NASA’s core values; safety and data-driven analysis remained at the forefront,” said Catherine Koerner, associate administrator, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “The updates to our mission plans are a positive step toward ensuring we can safely accomplish our objectives at the Moon and develop the technologies and capabilities needed for crewed Mars missions.”
NASA will continue stacking its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket elements, which began in November, and prepare it for integration with Orion for Artemis II.
Throughout the fall months, NASA, along with an independent review team, established the technical cause of an issue seen after the uncrewed Artemis I test flight in which charred material on the heat shield wore away differently than expected. Extensive analysis, including from more than 100 tests at unique facilities across the country, determined the heat shield on Artemis I did not allow for enough of the gases generated inside a material called Avcoat to escape, which caused some of the material to crack and break off. Avcoat is designed to wear away as it heats up and is a key material in the thermal protection system that guards Orion and its crew from the nearly 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit of temperatures that are generated when Orion returns from the Moon through Earth’s atmosphere. Although a crew was not inside Orion during Artemis I, data shows the temperature inside Orion remained comfortable and safe had crew been aboard.
Engineers already are assembling and integrating the Orion spacecraft for Artemis III based on lessons learned from Artemis I and implementing enhancements to how heat shields for crewed returns from lunar landing missions are manufactured to achieve uniformity and consistent permeability. The skip entry is needed for return from speeds expected for lunar landing missions.
“Victor, Christina, Jeremy, and I have been following every aspect of this decision and we are thankful for the openness of NASA to weigh all options and make decisions in the best interest of human spaceflight. We are excited to fly Artemis II and continue paving the way for sustained human exploration of the Moon and Mars,” said Reid Wiseman, NASA astronaut and Artemis II commander. “We were at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida recently and put eyes on our SLS rocket boosters, the core stage, and the Orion spacecraft. It is inspiring to see the scale of this effort, to meet the people working on this machine, and we can’t wait to fly it to the Moon.”
Wiseman, along with NASA astronauts Victor Glover and Christina Koch and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen, will fly aboard the 10-day Artemis II test flight around the Moon and back. The flight will provide valuable data about Orion systems needed to support crew on their journey to deep space and bring them safely home, including air revitalization in the cabin, manual flying capabilities, and how humans interact with other hardware and software in the spacecraft.
With Artemis, NASA will explore more of the Moon than ever before, learn how to live and work farther away from home, and prepare for future human exploration of the Red Planet. NASA’s SLS, exploration ground systems, and Orion spacecraft, along with the human landing system, next-generation spacesuits, Gateway lunar space station, and future rovers are NASA’s foundation for deep space exploration.
For more information about Artemis, visit:
-end-
Meira Bernstein / Rachel Kraft
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
meira.b.bernstein@nasa.gov / rachel.h.kraft@nasa.gov
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)