More Planets than Stars: Kepler’s Legacy
The Kepler mission enabled the discovery of thousands of exoplanets, revealing a deep truth about our place in the cosmos: there are more planets than stars in the Milky Way galaxy. The road to this fundamental change in our understanding of the universe, however, required almost 20 years of persistence before the mission became a […]

4 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
The Kepler mission enabled the discovery of thousands of exoplanets, revealing a deep truth about our place in the cosmos: there are more planets than stars in the Milky Way galaxy. The road to this fundamental change in our understanding of the universe, however, required almost 20 years of persistence before the mission became a reality with its selection in 2001.

Astronomers had assumed, but still had not confirmed, the existence of exoplanets when the mission concept that would become Kepler was first suggested in 1983. It wasn’t until the 1990s that the first confirmations of planets orbiting stars outside of our solar system were made, most of them gas giants orbiting close to their host star, not at all similar to what we know from our own solar system.
When Kepler launched in 2009, fewer than 400 exoplanets had been discovered. Today, there are more than 5,500 confirmed exoplanets and over half of them were discovered from Kepler data. Many of these confirmed exoplanets reside in the so-called “habitable zone” of their star, making them prime candidates for future observations to uncover more of the universe’s mysteries, including the potential for life.
The Kepler mission was designed to address the questions “How prevalent are other worlds?” and “How unique is our solar system?” Even if Kepler had found the opposite—that exoplanets were rare—Kepler still would have been an historic mission since the question it addressed was so scientifically profound.

Earlier versions of the mission proposal had been rejected four times beginning in 1992. Back then, the mission was known as the FRequency of Earth-Sized Inner Planets (FRESIP). After its second rejection in 1994, team members David Koch, Jill Tarter, and Carl Sagan, suggested the name change from FRESIP to Kepler.
One of the technical changes made to the 1994 proposal before the 1996 submission included changing the orbit from the Lagrange L2 point to a heliocentric orbit. This allowed Kepler to use reaction wheels for pointing the spacecraft, which reduced the thruster fuel consumption and saved on cost.
This wasn’t enough to convince NASA. To address concerns about the mission as proposed, two major demonstrations, one each after the 1996 and 1998 rejections, followed. The demonstrations reduced the risk that gave some reviewers pause and provided the Kepler team the opportunity to refine their operations.
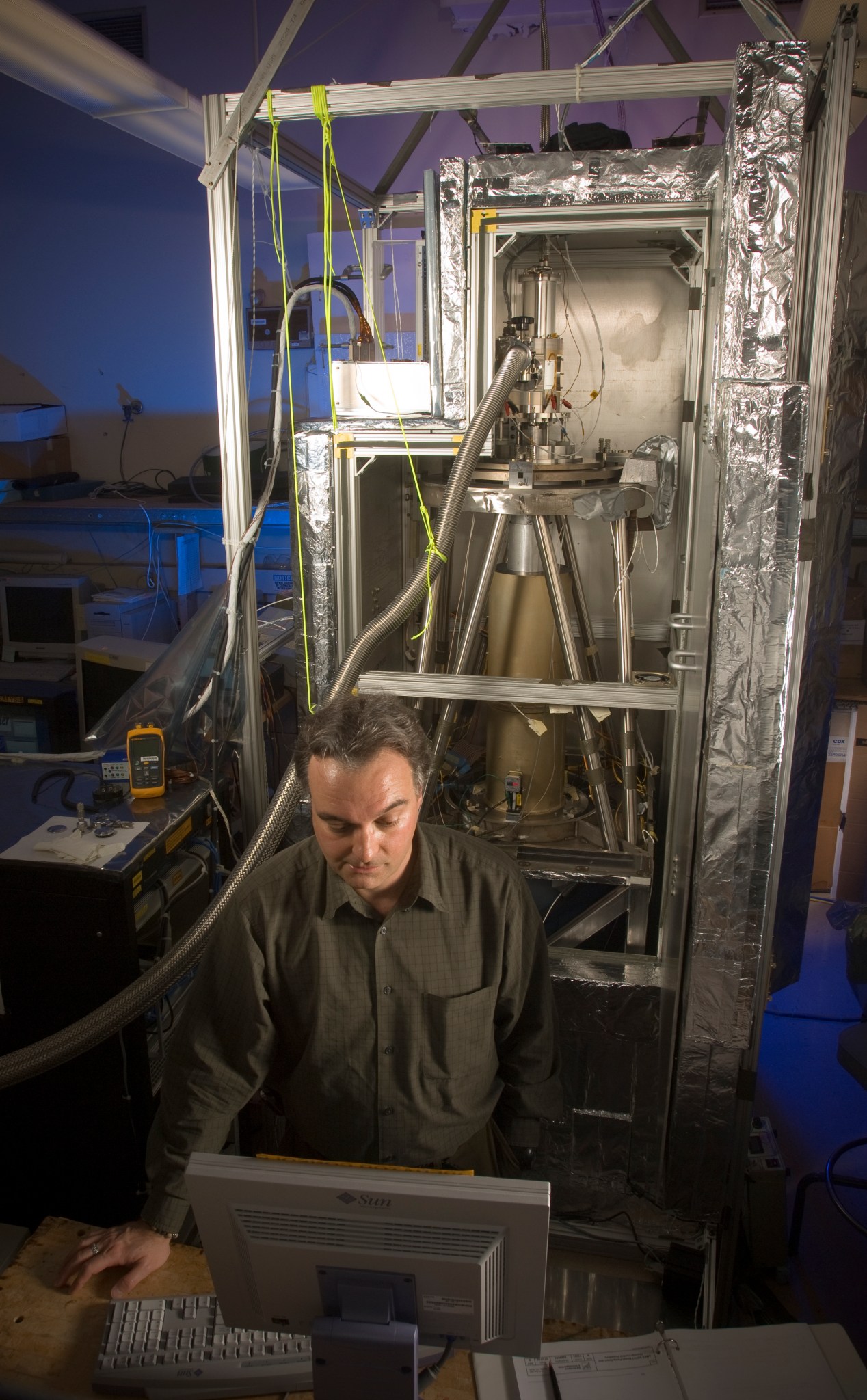

The first demonstration showed that the continuous, automatic monitoring of thousands of stars was possible. For that demonstration, an instrument called the Vulcan photometer was installed at Lick Observatory in California, which radioed its data to NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley for automated analysis. The second demonstration (following the 1998 rejection) was the construction of the Kepler Testbed Facility.
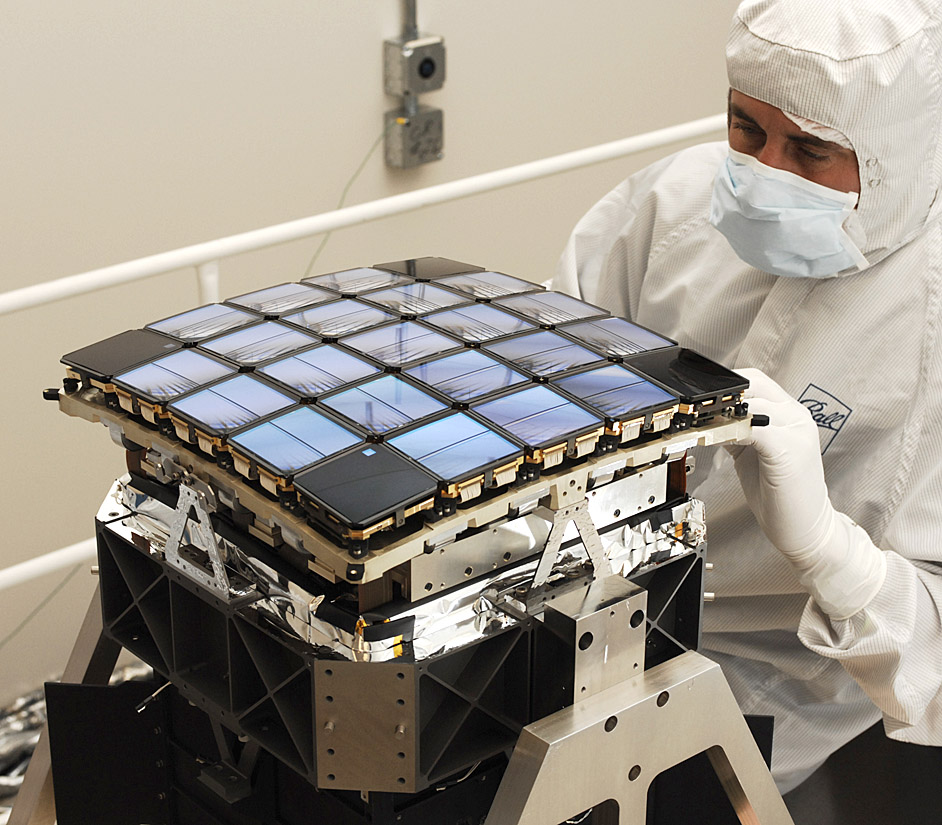
The testbed proved that existing charge-coupled device (CCD) technology no different from a consumer digital camera could achieve the precision necessary to detect Earth-size planets in the midst of the various kinds of noise expected in the whole system, from vibrations to image motion to cosmic ray strikes. The Kepler team at Ames built an intricate simulated sky and Ball Aerospace, the industry partner throughout the many years of proposals and the mission itself, built the numerical simulator for the demonstration. The testbed from the laboratory at Ames is now on display at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum.

These demonstrations finally put the remaining concerns to rest. In 2001, Kepler was selected more than 17 years after its principal investigator, William Borucki, had written a paper that considered a space-based photometer for detecting Earth-size planets with his colleague Audrey Summers of the Theoretical and Planetary Studies Branch in the Space Science Division at Ames.
In the eight years between selection and launch on March 6, 2009, the mission responded to a number of challenges and changes that were largely beyond the team’s control, such as NASA instituting a policy that required either NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland or the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to manage planetary missions, changes in accounting requirements, and increasing launch costs. Those pieces of Kepler’s story are told in detail in the latest book from the NASA History Office, NASA’s Discovery Program: The First Twenty Years of Competitive Planetary Exploration.
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)