May’s Night Sky Notes: Stargazing for Beginners
Were you inspired by the solar eclipse to become an amateur astronomer? If so, here are some high-level tips on how to get started, from Night Sky Notes!
3 min read
May’s Night Sky Notes: Stargazing for Beginners
by Kat Troche of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific
Millions were able to experience the solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, inspiring folks to become amateur astronomers – hooray! Now that you’ve been ‘bitten by the bug’, and you’ve decided to join your local astronomy club, here are some stargazing tips!
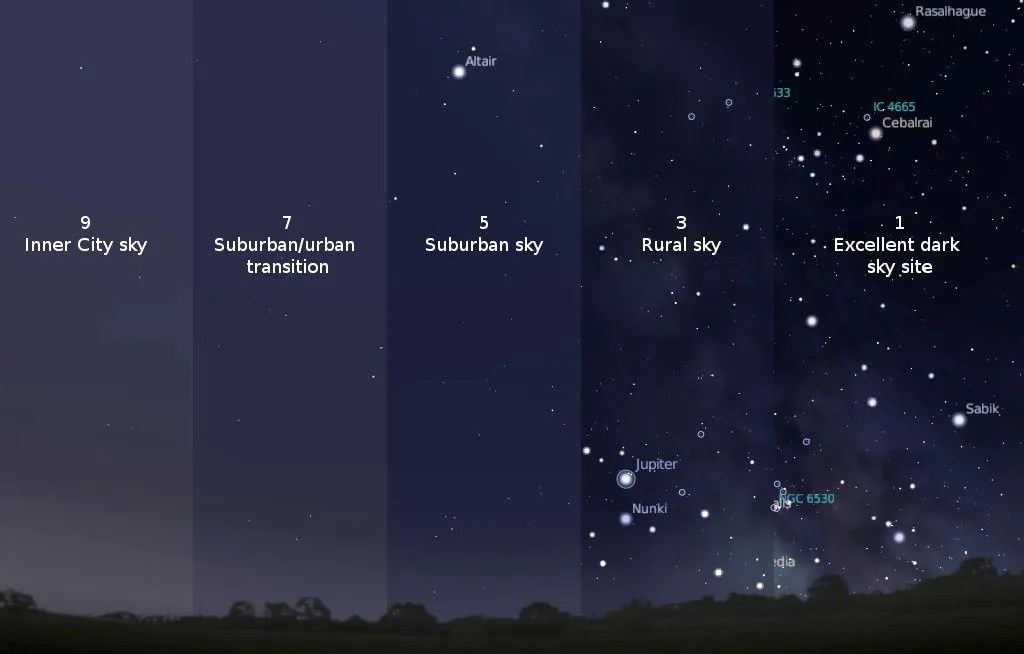
The Bortle Scale
Before you can stargaze, you’ll want to find a site with dark skies. It’s helpful learn what your Bortle scale is. But what is the Bortle scale? The Bortle scale is a numeric scale from 1-9, with 1 being darkest and 9 being extremely light polluted; that rates your night sky’s darkness. For example, New York City would be a Bortle 9, whereas Cherry Springs State Park in Pennsylvania is a Bortle 2.
Determining the Bortle scale of your night sky will help narrow down what you can expect to see after sunset. Of course, other factors such as weather (clouds namely) will impact seeing conditions, so plan ahead. Find Bortle ratings near you here: www.lightpollutionmap.info
No Equipment? No Problem!
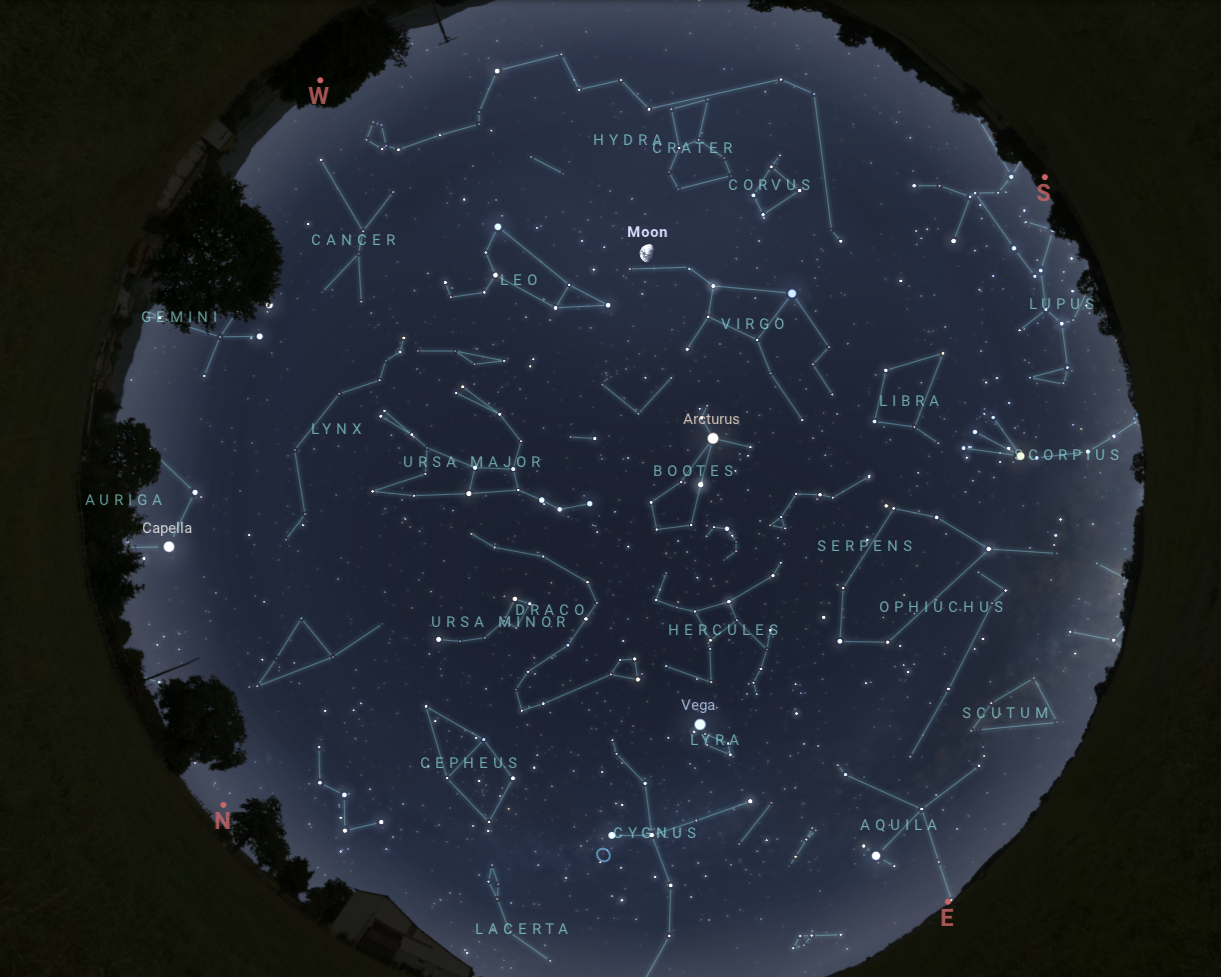
There’s plenty to see with your eyes alone. Get familiar with the night sky by studying star maps in books, or with a planisphere. These are great to begin identifying the overall shapes of constellations, and what is visible during various months.
Interactive sky maps, such as Stellarium Web, work well with mobile and desktop browsers, and are also great for learning the constellations in your hemisphere. There are also several astronomy apps on the market today that work with the GPS of your smartphone to give an accurate map of the night sky.
Keep track of Moon phases. Both the interactive sky maps and apps will also let you know when planets and our Moon are out! This is especially important because if you are trying to look for bright deep sky objects, like the Andromeda Galaxy or the Perseus Double Cluster, you want to avoid the Moon as much as possible. Moonlight in a dark sky area will be as bright as a streetlight, so plan accordingly! And if the Moon is out, check out this Skywatcher’s Guide to the Moon: bit.ly/MoonHandout
Put On That Red Light
If you’re looking at your phone, you won’t be able to see as much. Our eyes take approximately 30 minutes to get dark sky adapted, and a bright light can ruin our night vision temporarily. The easiest way to stay dark sky adapted is to avoid any bright lights from car headlights or your smartphone. To avoid this, simply use red lights, such as a red flashlight or headlamp.
The reason: white light constricts the pupils of your eyes, making it hard to see in the dark, whereas red light allows your pupils to stay dilated for longer. Most smartphones come with adaptability shortcuts that allow you to make your screen red, but if you don’t have that feature, use red cellophane on your screen and flashlight.
Up next: why binoculars can sometimes be the best starter telescope, with Night Sky Network’s upcoming mid-month article through NASA’s website!
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)