Margin’ up the Crater Rim!
To conclude its exploration of the mysterious margin unit before it ascends the rim of Jezero Crater, Perseverance made one last stop this past week to investigate these strange rocks at “Eremita Mesa.” Since beginning its steep drive up the crater rim, Perseverance has been traversing along the edge of the margin unit (the margin […]

2 min read
Margin’ up the Crater Rim!
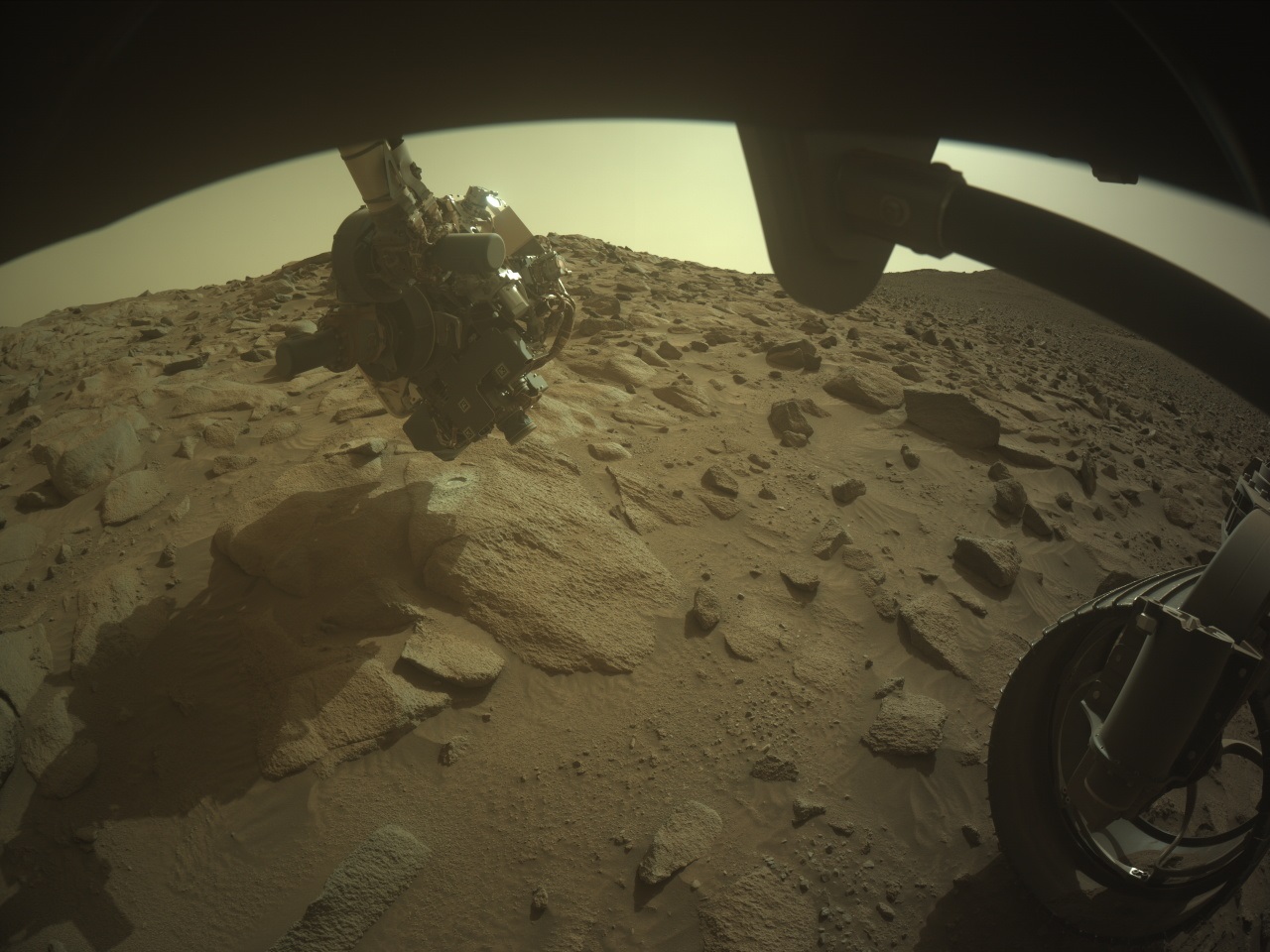

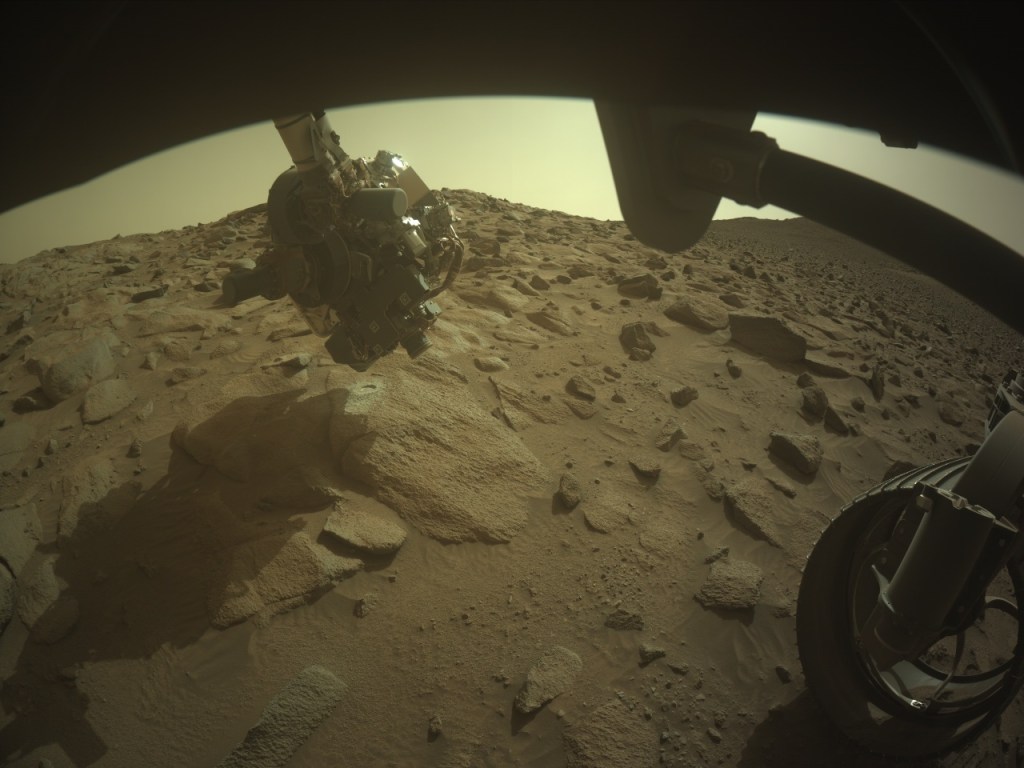
To conclude its exploration of the mysterious margin unit before it ascends the rim of Jezero Crater, Perseverance made one last stop this past week to investigate these strange rocks at “Eremita Mesa.”
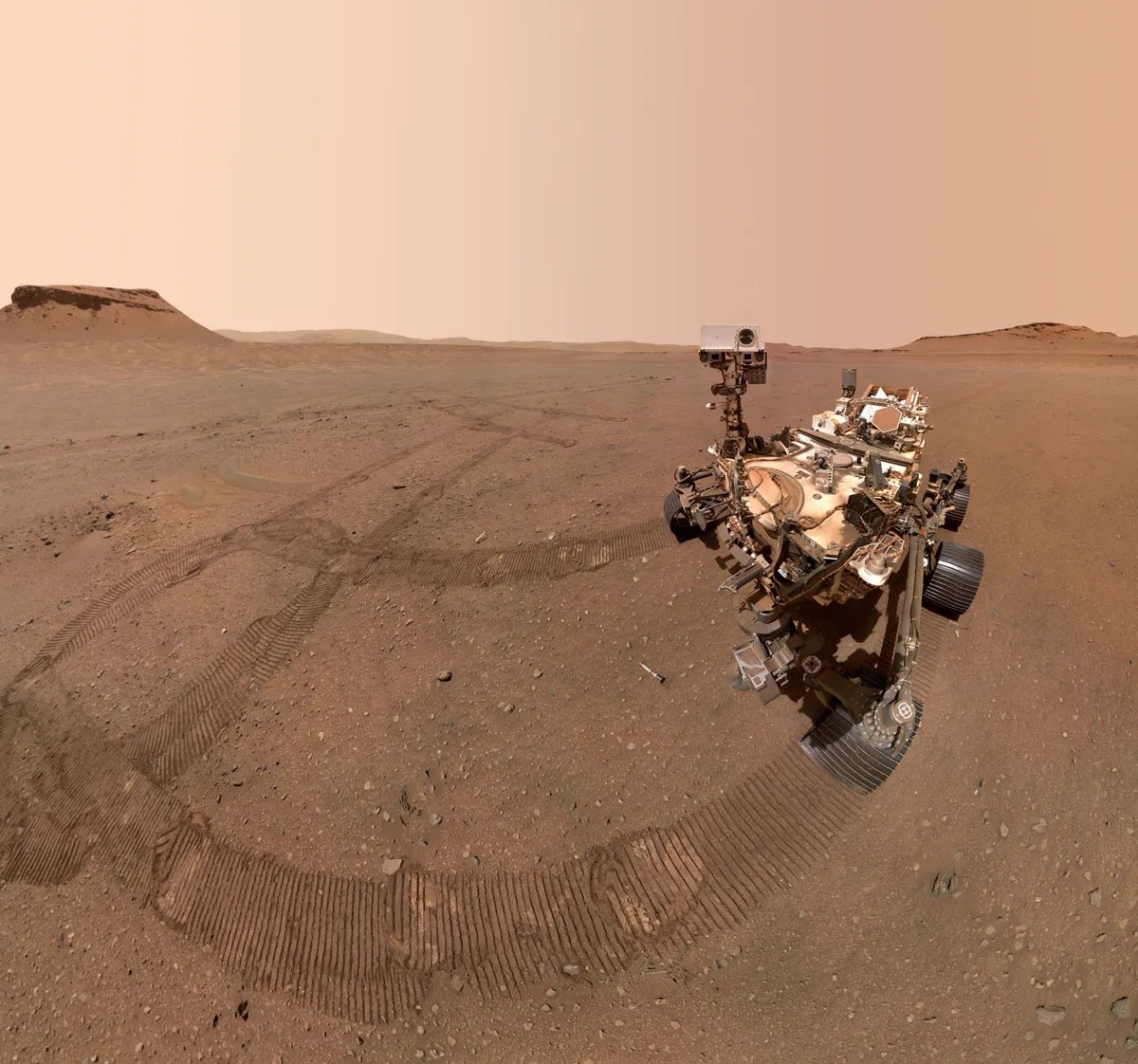
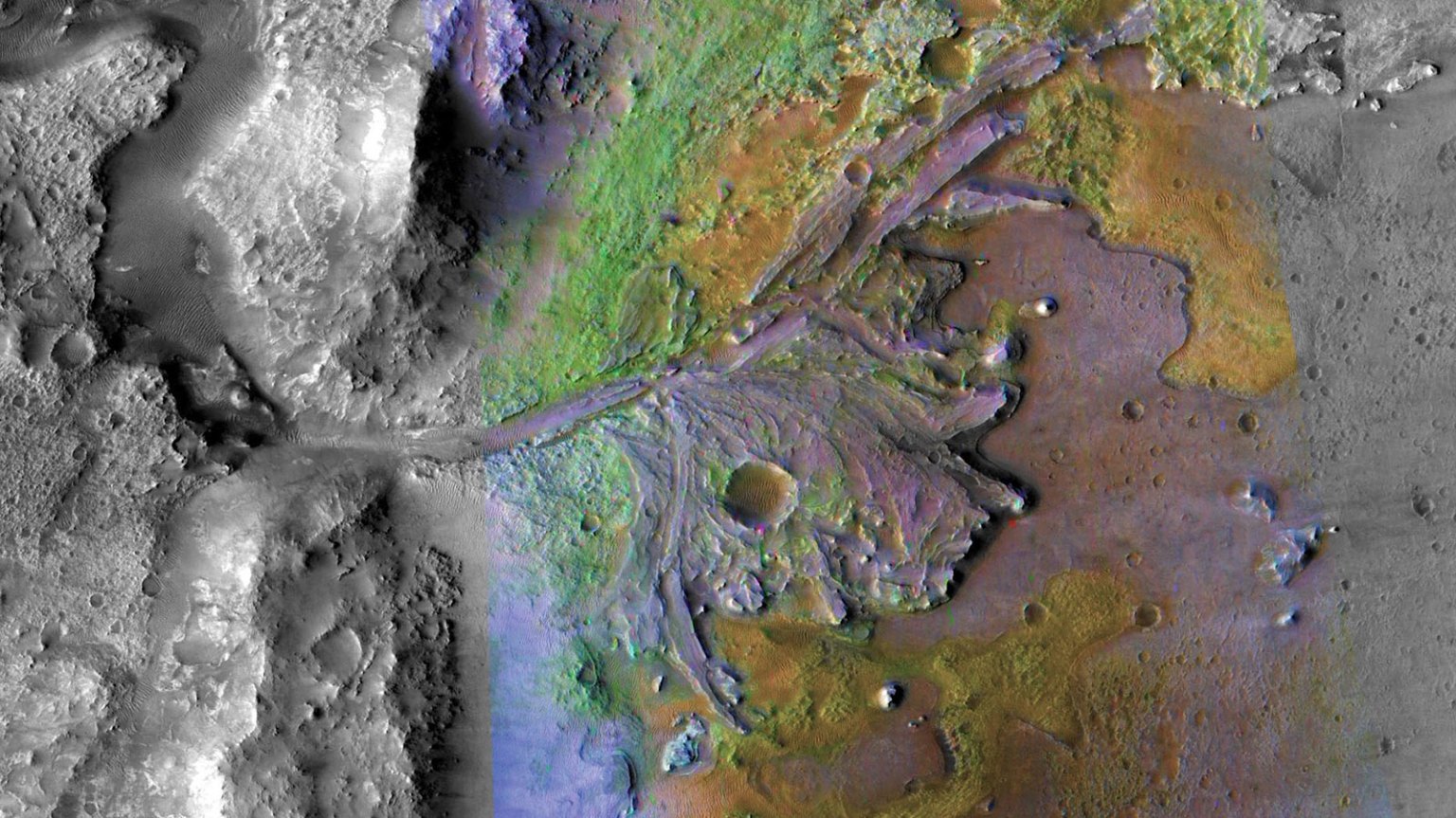
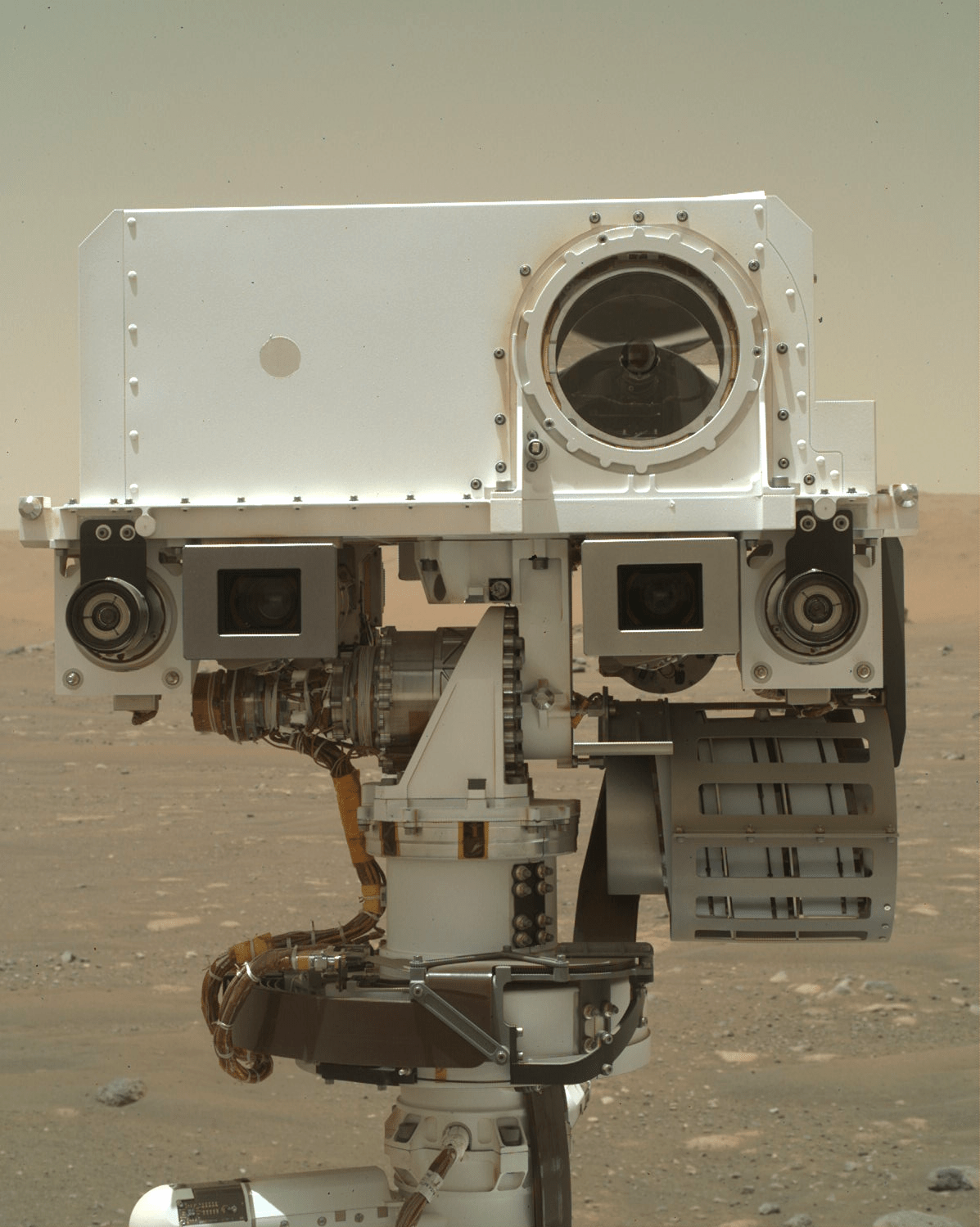
Since beginning its steep drive up the crater rim, Perseverance has been traversing along the edge of the margin unit (the margin of the margin!), an enigmatic unit rich in carbonates, a mineral group closely linked to habitability. Here, the rover team scouted out a mound of rock called “Specter Chasm,” where Perseverance cleared away the dusty, weathered surface with its trusty abrading bit. The resulting abraded patch, called Eremita Mesa, is pictured above being investigated by Perseverance’s proximity science instruments mounted on its robotic arm. This includes taking close-up images to examine the millimeter-scale particles that make up the rock, using the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera, which functions as Perseverance’s magnifying glass.
Before the rover began exploring, investigations using orbital satellite data had suggested the margin unit rocks may have formed in several different ways. Theories the team has been exploring include that the unit formed on the shoreline of the ancient lake that once filled Jezero Crater, or instead that it was produced by volcanic processes such as pyroclastic flows or ashfall, or ancient lavas flowing into the crater. Since Perseverance began its investigation of the unit in September 2023, more than 350 sols ago (1 sol = 1 Mars day), the Science Team has been scouring data collected by the rover’s instruments to help constrain the unit’s origin. So far, this has remained largely a mystery, with the original rock textures potentially heavily affected by alteration since it formed more than 3 billion years ago. Perseverance has already collected three exciting samples of this curious rock unit for future Earth return: “Pelican Point,” “Lefroy Bay,” and “Comet Geyser,” and the team is hoping the data collected at Eremita Mesa could help further constrain the ancient processes on Mars that formed these strange rocks.
Next, it’s onwards and upwards for Perseverance as it faces a steep climb up the crater rim, where perhaps even more exotic and exciting rocks await!
Written by Alex Jones, Ph.D. student at Imperial College London
Share
Details
Related Terms
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)