Hubble Takes a Look at Tangled Galaxies
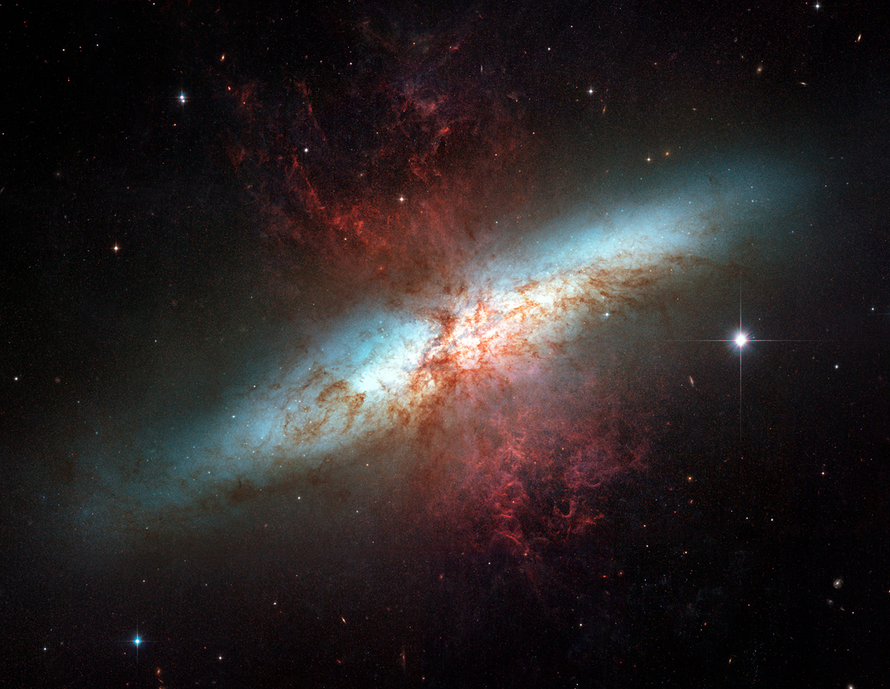
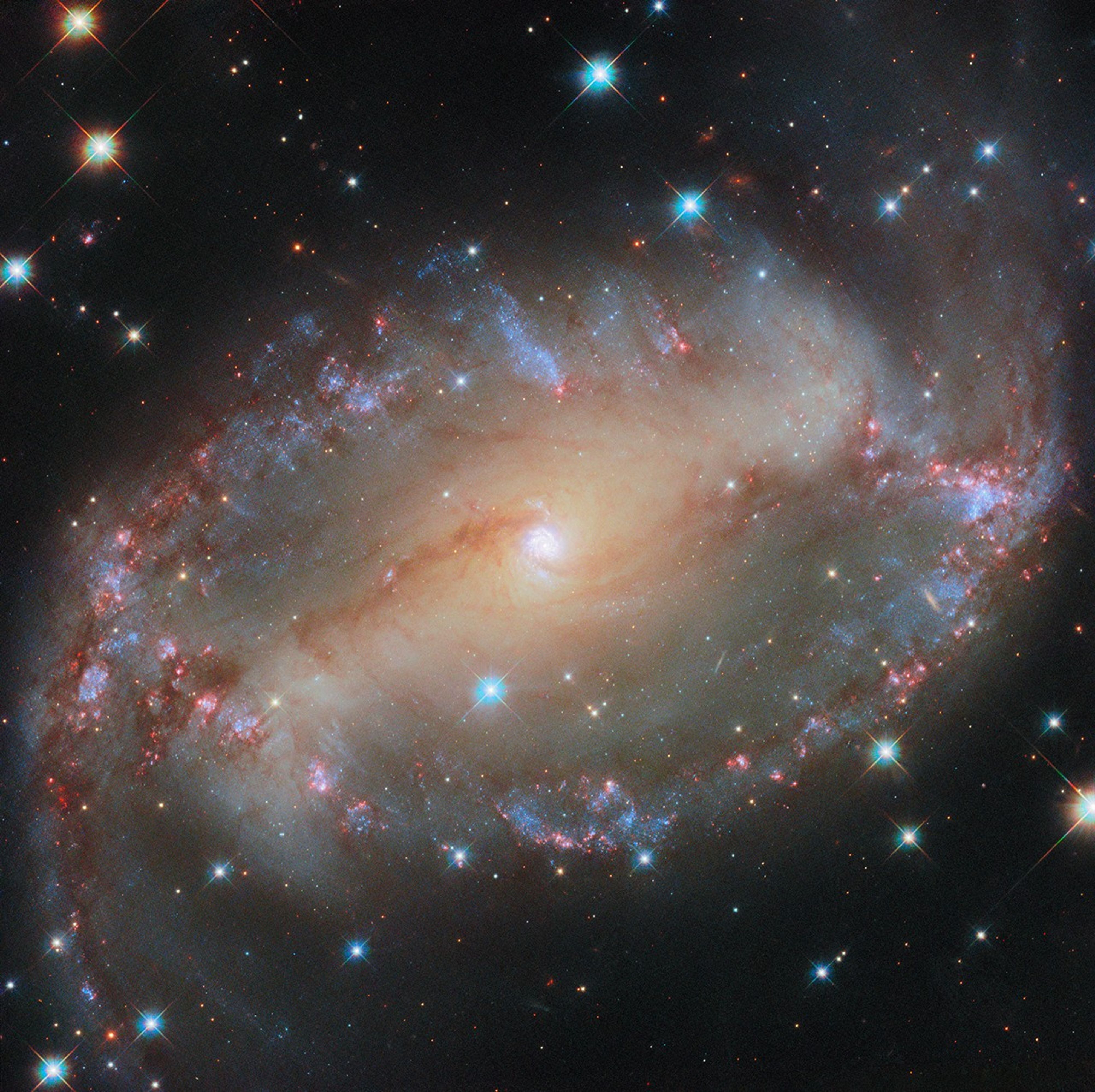
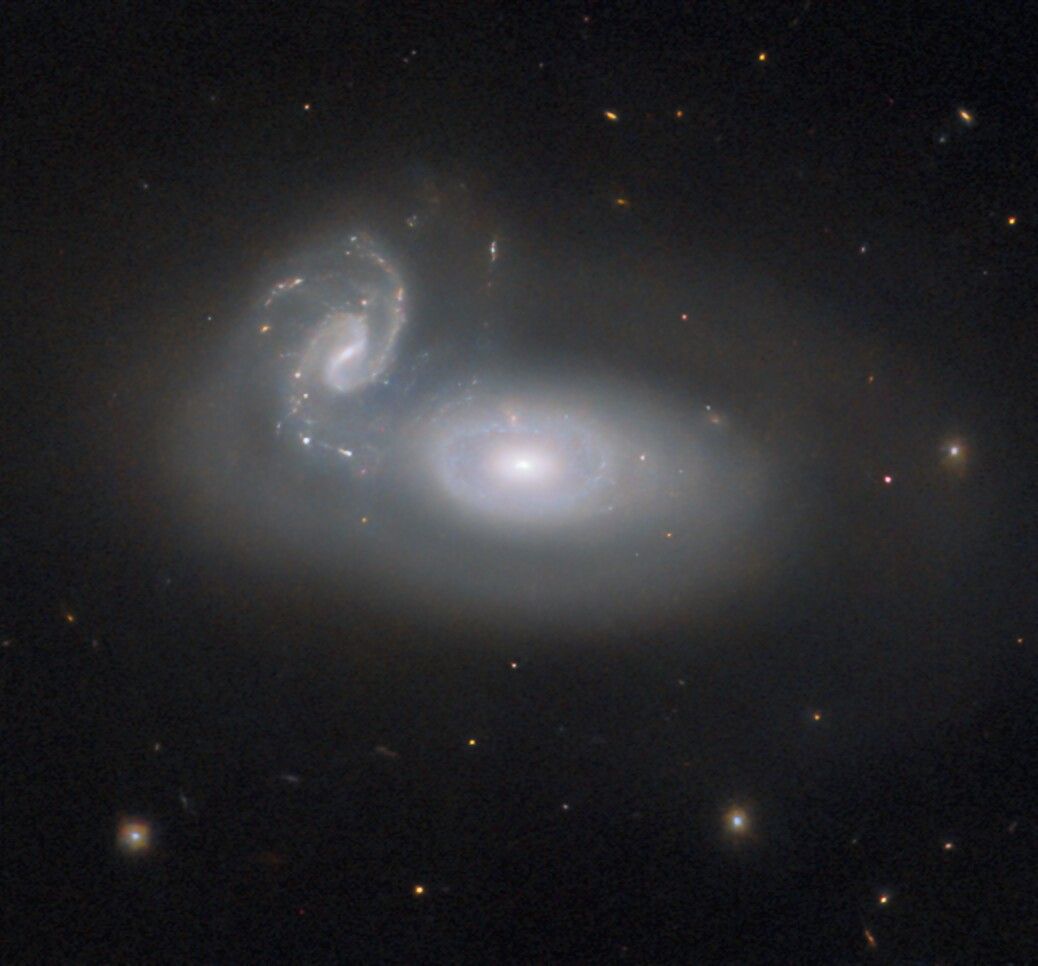
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image depicts the cosmic tangle that is MCG+05-31-045, a pair of interacting galaxies located 390 million light-years away and a part of the Coma galaxy cluster. The Coma Cluster is a particularly rich cluster that contains over a thousand known galaxies. Amateur astronomers can easily spot several of these in […]

2 min read
Hubble Takes a Look at Tangled Galaxies
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image depicts the cosmic tangle that is MCG+05-31-045, a pair of interacting galaxies located 390 million light-years away and a part of the Coma galaxy cluster.
The Coma Cluster is a particularly rich cluster that contains over a thousand known galaxies. Amateur astronomers can easily spot several of these in a backyard telescope (See Caldwell 35). Most of them are elliptical galaxies, and that’s typical of a dense galaxy cluster like the Coma Cluster: many elliptical galaxies form through close encounters between galaxies that stir them up, or even collisions that rip them apart. While the stars in interacting galaxies can stay together, their gas is twisted and compressed by gravitational forces and rapidly used up to form new stars. When the hot, massive, blue stars die, there is little gas left to form new generations of young stars to replace them. As spiral galaxies interact, gravity disrupts the regular orbits that produce their striking spiral arms. Whether through mergers or simple near misses, the result is a galaxy almost devoid of gas, with aging stars orbiting in uncoordinated circles: an elliptical galaxy.
It’s very likely that a similar fate will befall MCG+05-31-045. As the smaller spiral galaxy is torn up and integrated into the larger galaxy, many new stars will form, and the hot, blue ones will quickly burn out, leaving cooler, redder stars behind in an elliptical galaxy, much like others in the Coma Cluster. But this process won’t be complete for many millions of years.
Explore more Coma Cluster images from Hubble.
- Hubble Uncovers Thousands of Globular Star Clusters Scattered Among Galaxies
- Hubble’s Galaxies With Knots, Bursts
- Hubble Sees Near and Far
- Hubble Sees Plunging Galaxy Losing Its Gas
- Hubble Catches Galaxies Swarmed by Star Clusters
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)