Hubble Examines Stars Ensconced in a Cocoon of Gas
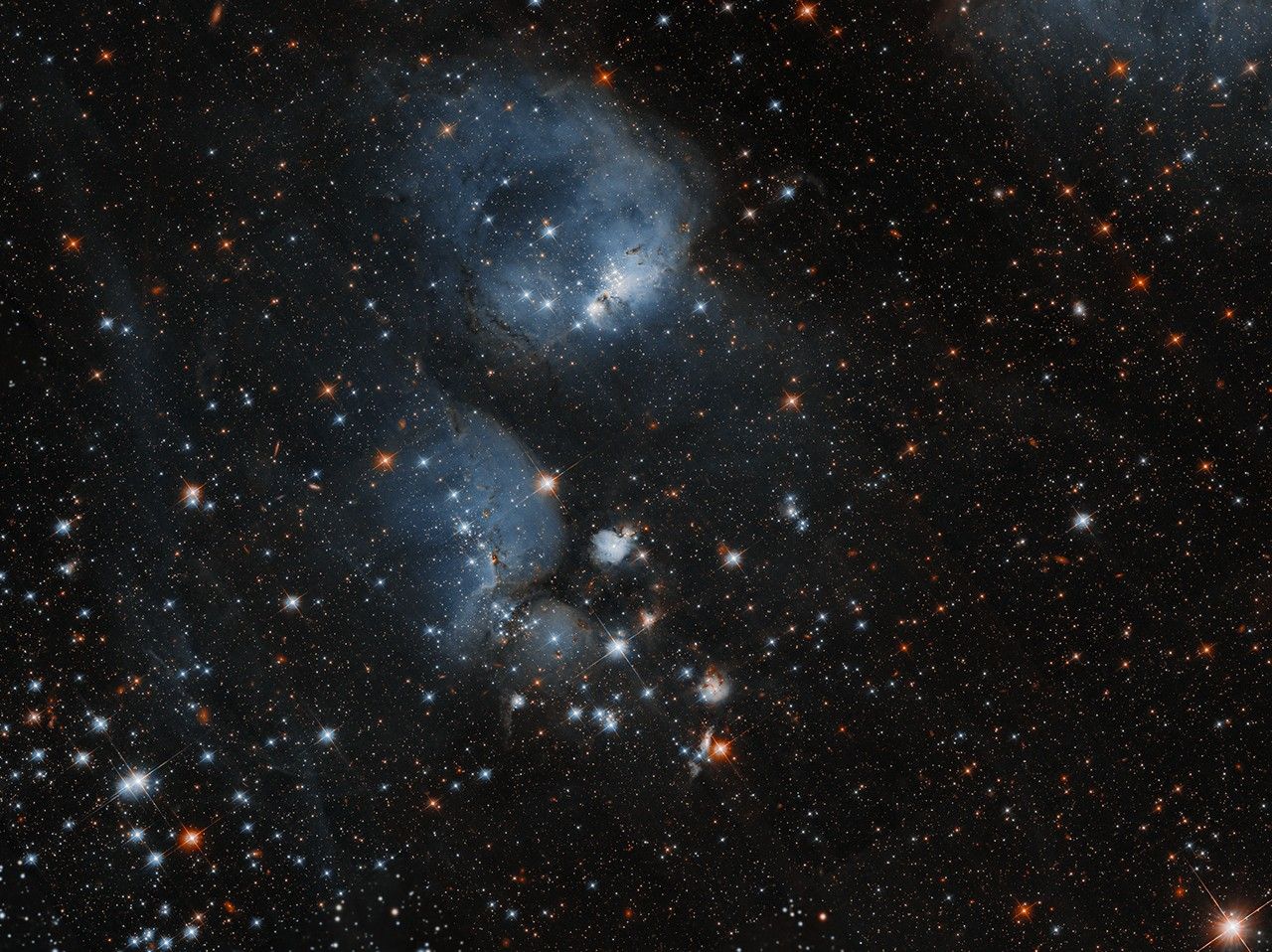
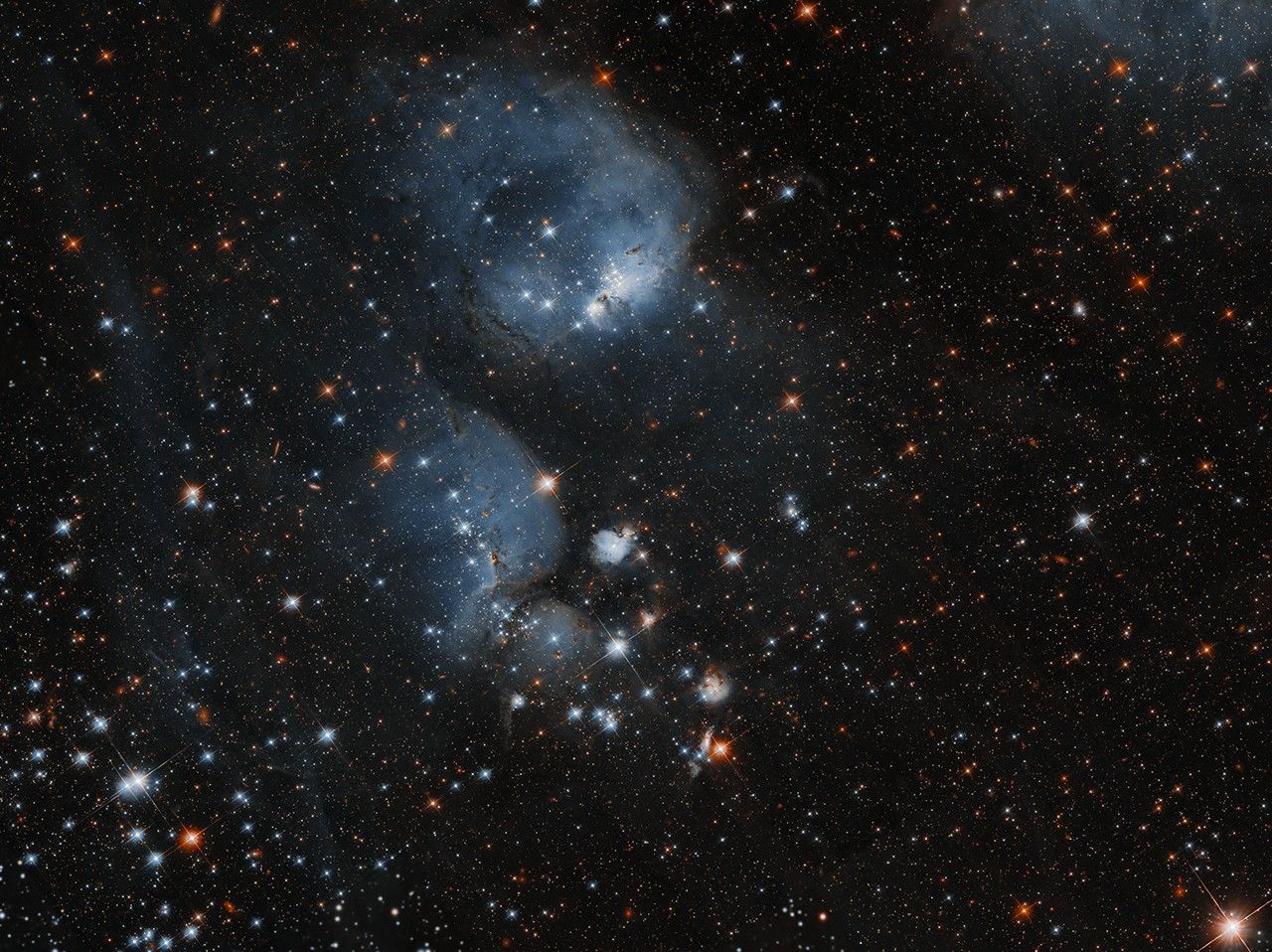
An open cluster of stars shines through misty, cocoon-like gas clouds in this Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 460. NGC 460 is located in a region of the Small Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. This particular region contains a number of young star clusters and nebulae of different sizes […]

2 min read
Hubble Examines Stars Ensconced in a Cocoon of Gas
An open cluster of stars shines through misty, cocoon-like gas clouds in this Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 460.
NGC 460 is located in a region of the Small Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy that orbits the Milky Way. This particular region contains a number of young star clusters and nebulae of different sizes ― all likely related to each other. The clouds of gas and dust can give rise to stars as portions of them collapse, and radiation and stellar winds from those hot, young bright stars in turn shape and compress the clouds, triggering new waves of star formation. The hydrogen clouds are ionized by the radiation of nearby stars, causing them to glow.
The NGC 460 star cluster resides in one of the youngest parts of this interconnected complex of stellar clusters and nebulae, which is also home to a number of O-type stars: the brightest, hottest and most massive of the normal, hydrogen-burning stars (called main-sequence stars) like our Sun. O-type stars are rare ― out of more than 4 billion stars in the Milky Way, only about 20,000 are estimated to be O-type stars. The area that holds NGC 460, known as N83, may have been created when two hydrogen clouds in the region collided with one another, creating several O-type stars and nebulae.
Open clusters like NGC 460 are made of anywhere from a few dozen to a few thousand stars loosely knitted together by gravity. Open clusters generally contain young stars, which may migrate outward into their galaxies as time progresses. NGC 460’s stars may someday disperse into the Small Magellanic Cloud, one of the Milky Way’s closest galactic neighbors at about 200,000 light-years away. Because it is both close and bright, it offers an opportunity to study phenomena that are difficult to examine in more distant galaxies.
Six overlapping observations from a study of the gas and dust between stars, called the interstellar medium, were combined to create this Hubble image. The study aims to understand how gravitational forces between interacting galaxies can foster bursts of star formation. This highly detailed 65 megapixel mosaic includes both visible and infrared wavelengths. Download the 400 MB file and zoom in to see some of the intricacies captured by Hubble.
Explore More
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
What's Your Reaction?



















.jpg?#)